What Is A Roof Joist? [2025]

Are you someone who is trying to understand how the roof joists of a shed or canopy work? 🙋♂️🙋♂️
To be honest with you, there are a lot of engineering steps involved in designing roof joists.
But this is what this post is for. We’ll tell you everything we know about roof joists and reference more detailed guides where necessary. 🧑🏫🧑🏫
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll show what a roof joist is, how it works and how to design roof joists. 🔥🔥
So let’s get started. 🚀🚀
Definition – What Is A Roof Joist?
A roof joist is a structural element of a roof which is aligned horizontally. It withstands loads such as wind, snow, dead and live load and distributes those loads to its supports, primary beams, walls or columns.
Don’t mix up roof joist with ceiling joist. These elements are similar but not the same. We’ll explain the differences later in this article.
So, the material of roof joists can be timber, steel or concrete. Timber, however, is the most common.
Let’s have a look at a visualization of roof joists. 👇👇
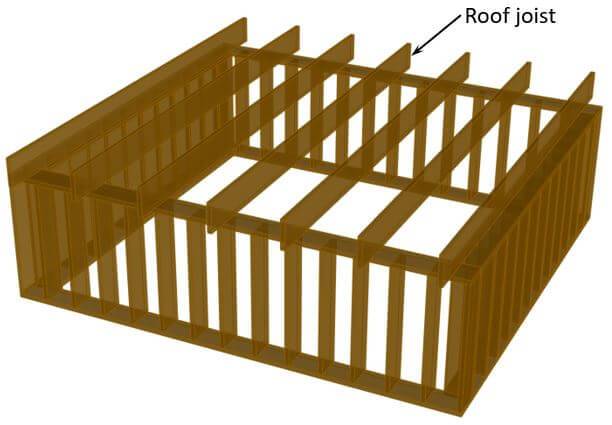
The roof joists run parallel to each other and are spaced apart at regular intervals s (in this case). Usually the spacing is between 0.5 m and 1.2 m. But in special cases it could also be higher or lower.
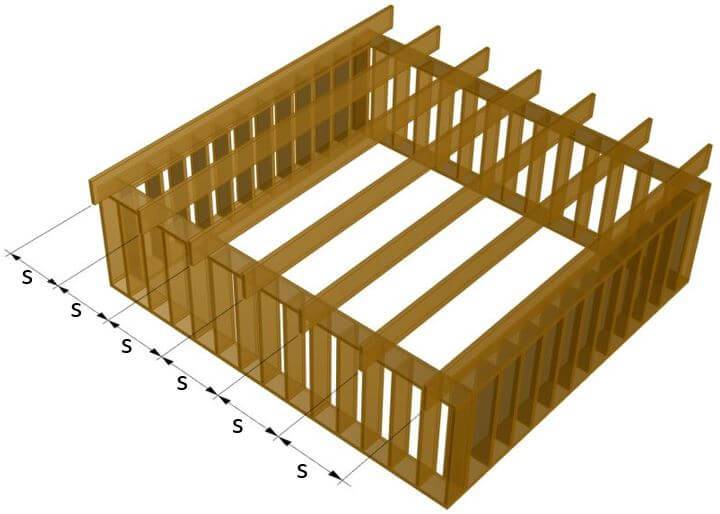

The size, shape, spacing, and material of the roof joists depend on many factors such as the size of the building and therefore the span of the joists, location and loads.
How Does A Roof Joist Work?
Basically the roof joists job is to
- Take up all the loads that act on the roof
- Not break 😃😃
- And distribute the loads/forces further to its support and later to the foundations.
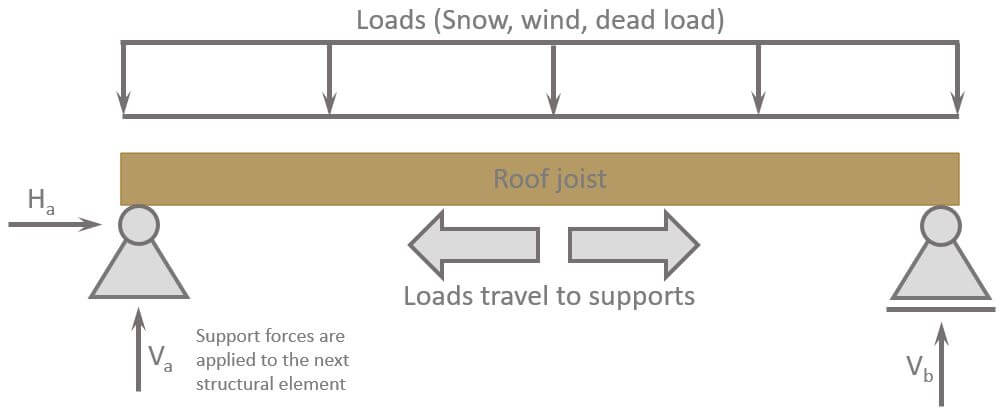
Alright, but now let’s look at how we design and dimension roof joists. 👇👇
Design Of Roof Joists
First of all: We wrote an extensive article about how to design timber beams and timber flat roof beams.
Roof joists are basically beams. The word beam is just the term used in structural engineering.
While we’ll go into detail in the other 2 blog posts, we’ll write down the steps that need to be done to design the roof joist:
- Calculate the loads (snow, wind, dead, live load)
- Calculate the design loads with load combinations
- Definition of timber properties
- Assumption of width and height of beam
- Calculation of the internal forces (N, V, M)
- ULS Design
- SLS Design
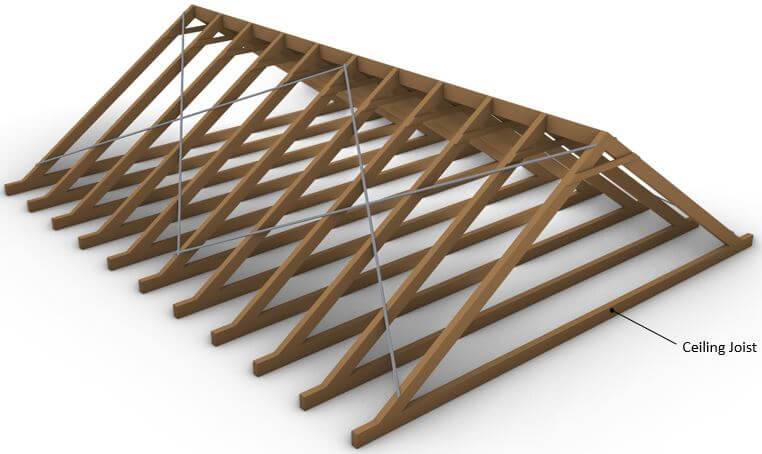
Roof Joist And Ceiling Joist – The Differences
Roof joists can only be in one level of a building/structure – the top.
But ceiling joists can be in multiple. And you can even call the roof joists ceiling joists.
However, the other way around doesn’t work!
Alright, so let’s look at some examples where ceiling joists are used.
Rafter Roof

Collar Beam Roof

Conclusion
Now, you got an understanding of what roof joists are. If you want to know more about how structural systems work, then I recommend checking out one of the following resources. 👇👇
- Understand what different types of loads act on joists/beams
- Learn what supports are
- Calculate internal forces
Those are the basics in structural engineering. Once you understand them, you can go further and learn about loads:
And load combinations.
Then, finally, structural elements can be designed with different materials based on the internal forces. Check out our structural guides. 👇👇
I hope that this article helped you understand roof joists. In case you still have questions, let us know in the comments below. ✍️✍️
Roof Joist FAQ
Roof joists are structural elements that support the weight of a roof and the loads applied to a roof. The joists then transfer the loads to walls or columns of a building. Joists are usually made of wood or steel.
Size and spacing of roof joists depend on many factors such as location, loads, span, weight of the roof and location of the walls or columns. A structural engineer needs to calculate the required size and spacing of roof joists based on these factors.
![9+ Polar Moment Of Inertia Formulas [2025]](https://www.structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/2nd-polar-moment-of-inertia-formulas-768x439.jpg)
![Moment of Inertia Calculation [2025]](https://www.structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Moment-of-Inertia-calculation-768x439.jpg)

![How to Calculate The Cross Sectional Area? [A Beginner’s Guide]](https://www.structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/how-to-calculate-the-cross-sectional-area-768x439.jpg)