13 Beam Deflection Formulas
Calculating reaction forces, internal forces and deflections of beams for different loading scenarios, is one of the things in structural engineering that we do throughout our studies and also careers later on.
While it’s very important to know how to calculate reaction and internal forces, it’s much more difficult to calculate the deflection of beams due to different loads.
In case it’s not a simply supported beam, you most likely have to either look up the formula from a book or use an advanced FEM program.
In this article, we’ll show, the most Important and Easiest Deflection Formulas for Beams due to different loading scenarios like UDL line loads, point loads and external moments.
Now, before we get started, the unit of the deflection is in most cases [mm] for most European countries.
But now, let’s jump into it.
Simply Supported Beam: Uniformly Distributed Line Load
This is the most used static system and deflection formulas🔥.
Line Load | Simply Supported Beam
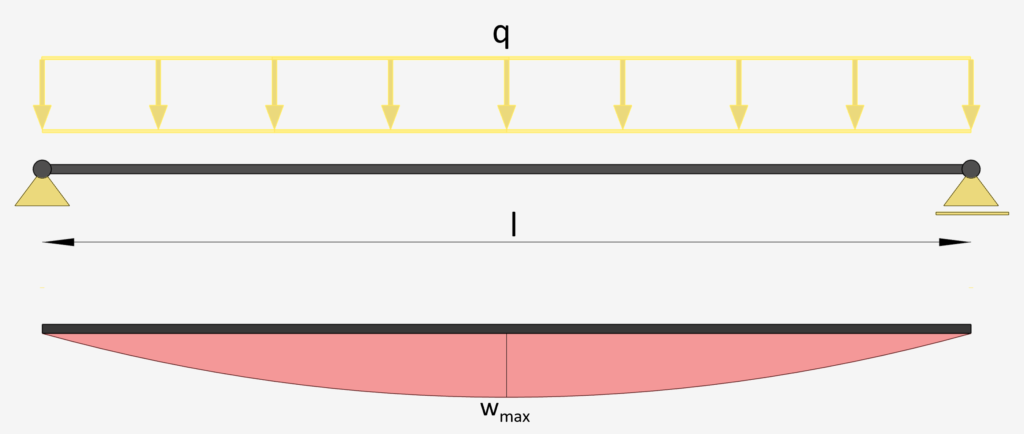
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{5}{384} \cdot \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
Here are some practical examples of the simply supported beam
Simply Supported Beam: Point Load on Midspan
Point Load Midspan | Simply Supported Beam
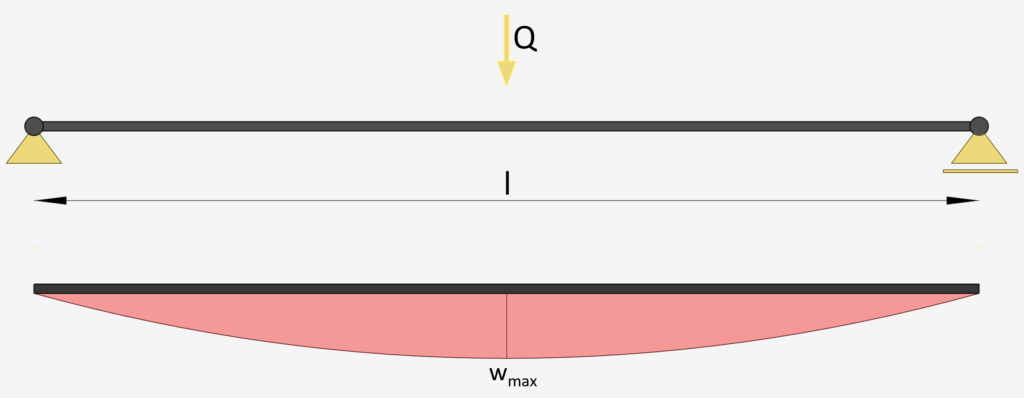
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{Ql^3}{48EI}$
Here is a practical example of the simply supported beam with a Point Load
Simply Supported Beam: Intermediate Point Load
Intermediate Point Load | Simply Supported Beam
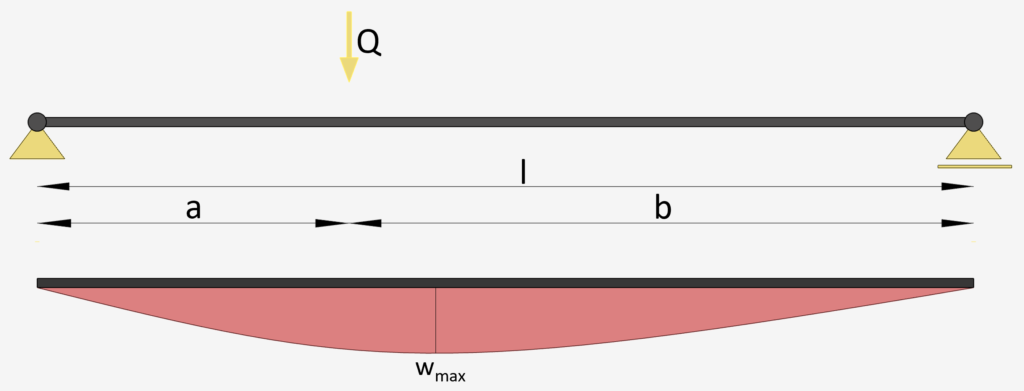
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{Qa\cdot(l^2-a^2)^{3/2}}{9l\cdot \sqrt{3}\cdot EI}$ if a<b
Here is a practical example of the simply supported beam with a Point Load
Simply Supported Beam: Moment on 1 End
1 External Moment | Simply Supported Beam
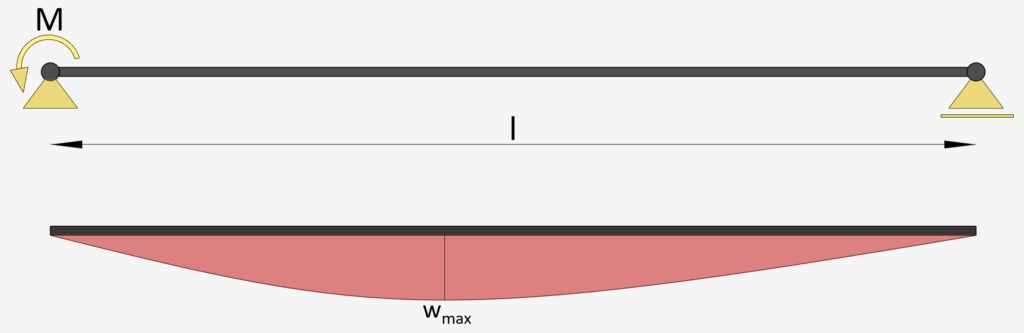
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{M\cdot l^2}{9\cdot \sqrt{3}\cdot EI}$
Simply Supported Beam: 2 Point Loads
2 Point Loads | Simply Supported Beam
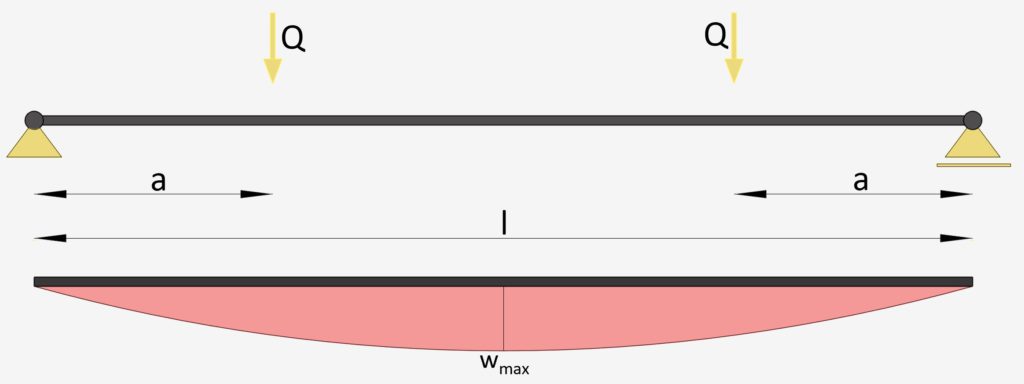
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{F\cdot a}{24\cdot EI} \cdot (3l^2-4a^2)$
Cantilever Beam: Uniformly Distributed Line Load (UDL)
Line Load | Cantilever Beam
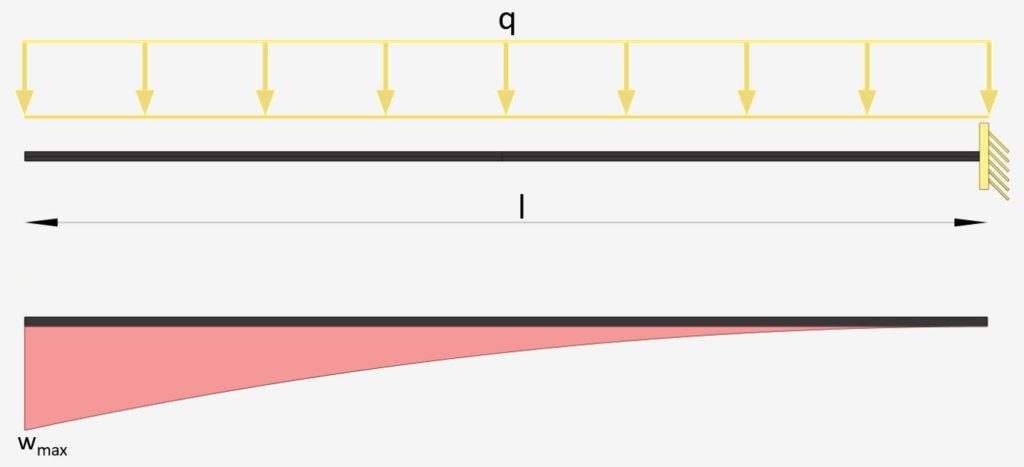
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{ql^4}{8\cdot EI}$
Cantilever Beam: Point Load at Free End
Point Load – Free End | Cantilever Beam
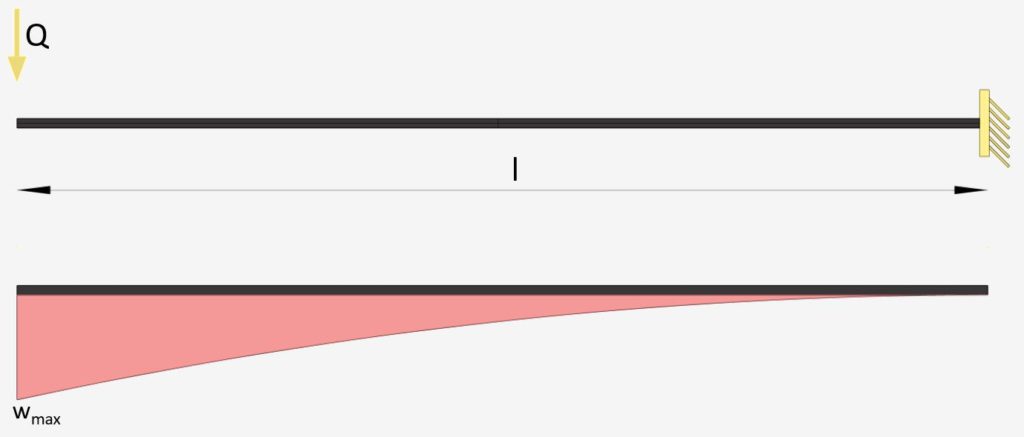
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{Ql^3}{3\cdot EI}$
Cantilever Beam: Intermediate Point Load
Intermediate Point Load | Cantilever Beam
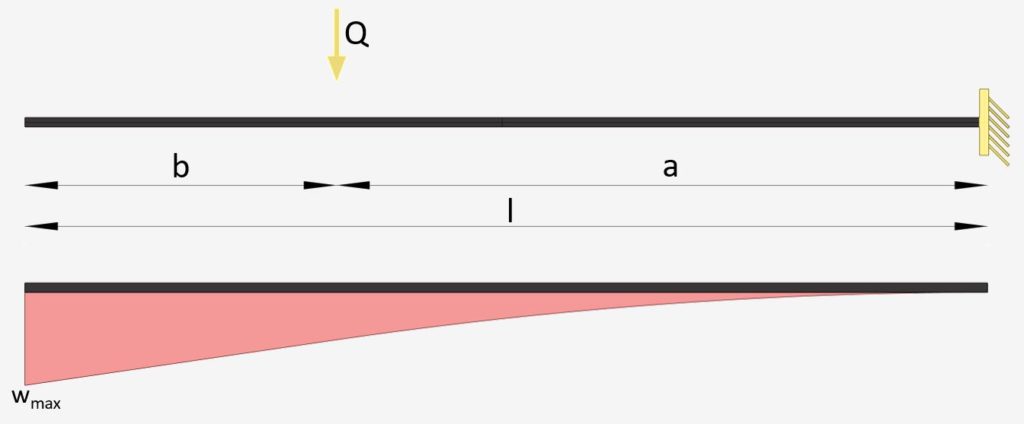
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{max} = \frac{Qa^3}{6\cdot EI}\cdot (3l-a)$
2-Span Continuous Beam: Uniformly Distributed Line Load
UDL Line Load | Continuous Beam Deflection
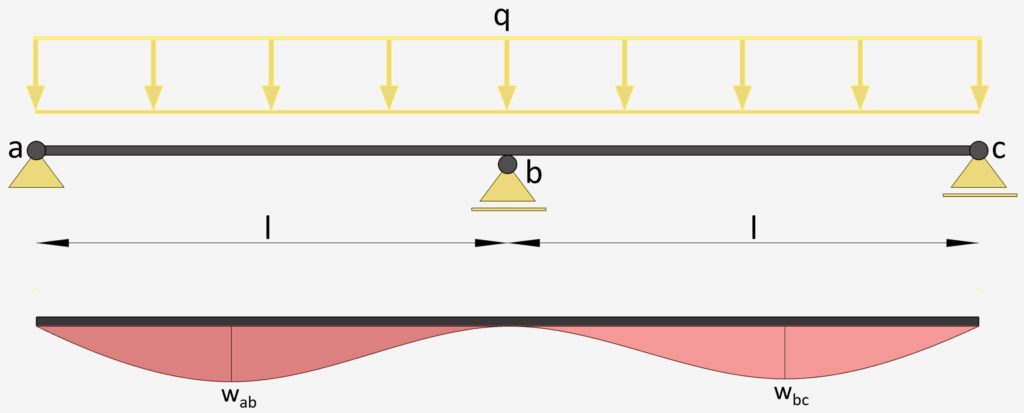
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{ab} = 0.00521 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
$w_{bc} = 0.00521 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
E = E-modulus of the Beam Material
I = Moment of Inertia of Beam
2-Span Continuous Beam: Uniformly Distributed Line Load on 1 span
UDL Line Load on 1 span | Continuous Beam
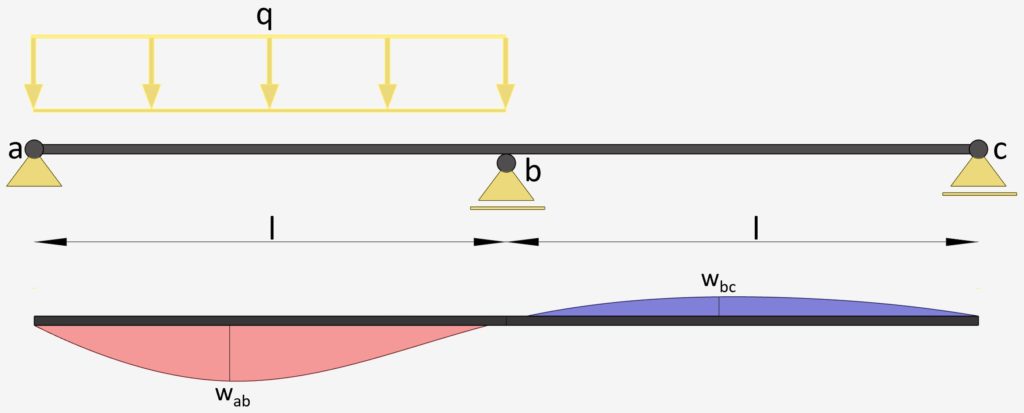
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{ab} = 0.00911 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
$w_{bc} = -0.00391 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
E = E-modulus of the Beam Material
I = Moment of Inertia of Beam
2-Span Continuous Beam: Point Load on 1 span
Point Load on 1 span | Continuous Beam
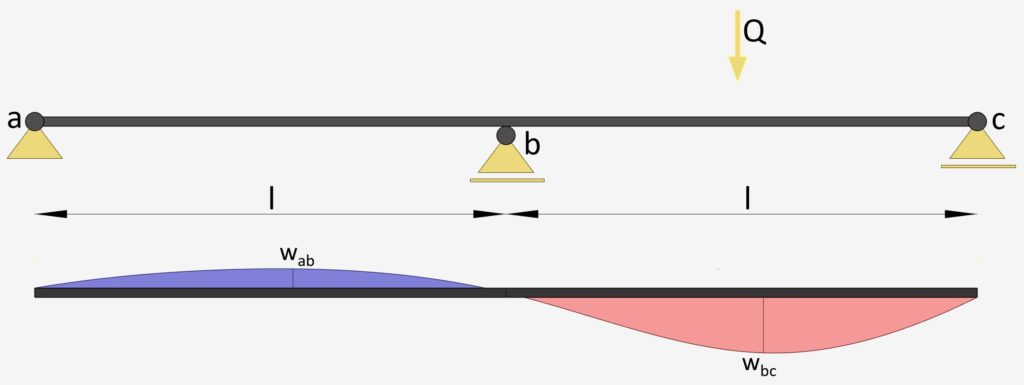
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{ab} = -0.00588 \frac{Ql^3}{EI}$
$w_{bc} = 0.01495 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
E = E-modulus of the Beam Material
I = Moment of Inertia of Beam
3-Span Continuous Beam: Uniformly Distributed Line Load
UDL Line Load | Continuous Beam Deflection
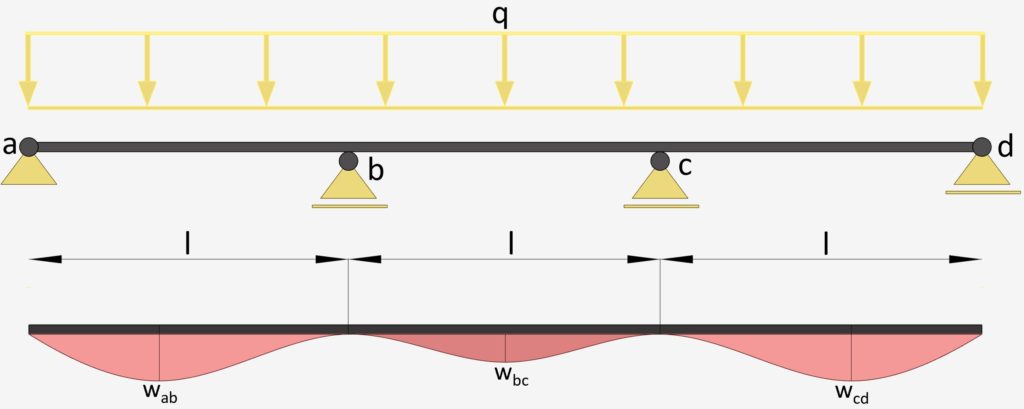
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{ab} = w_{cd} = 0.00677 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
$w_{bc} = 0.00052 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
E = E-modulus of the Beam Material
I = Moment of Inertia of Beam
3-Span Continuous Beam: Uniformly Distributed Line Load on Center Span
UDL Line Load on Center | Continuous Beam Deflection
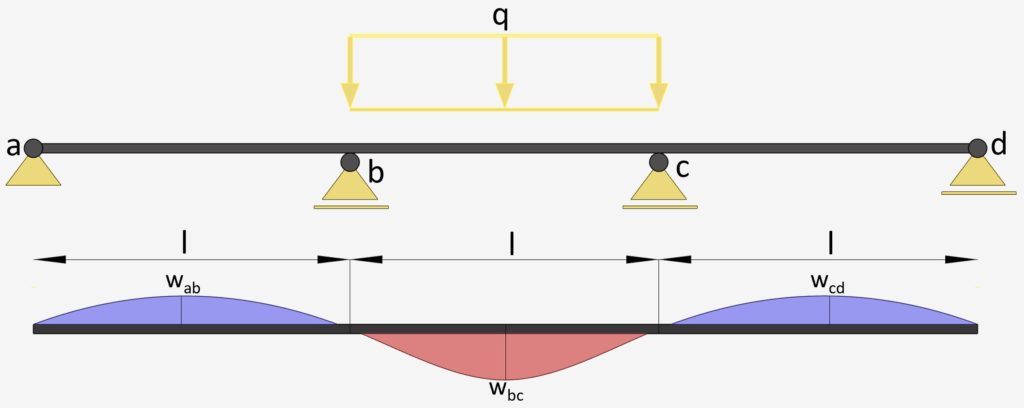
Max. Deflection $w_{max}$
$w_{ab} = w_{cd} = -0.00313 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
$w_{bc} = 0.00677 \frac{ql^4}{EI}$
E = E-modulus of the Beam Material
I = Moment of Inertia of Beam
If you are new to structural design, then check out our design tutorials where you can learn how to use the deflection of beams to design structural elements such as
Do you miss any deflection formulas for beams that we forgot in this article? Let us know in the comments✍️
![Timber Truss Roof Design [A Structural Guide]](https://www.structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Timber-Truss-Roof-Design-768x439.jpg)
![Understand Shear Forces [An Engineering Explanation]](https://www.structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Shear-force-768x439.jpg)